





|
|
|

|
|

|

|

|

|
Derivative Definition & Function
Notation
Tangent Line
Differentiability
First Derivative Use
Second Derivative Use
Arithmetic Properties
Product Rule
Quotient Rule
Power Rule
Mean Value Theorem for Derivatives
Implicit Differentiation (Chain Rule)
Derivative of an Inverse Function
L'Hôpital's Rule
Derivative of $e$ Exponents
Derivative of Logarithmic Functions
Derivative of Exponential Functions
Derivative of a Variable Raised to Itself
$d/d\theta\sin(\theta)$
$d/d\theta\cos(\theta)$
$d/d\theta\tan(\theta)$
$d/d\theta\cot(\theta)$
$d/d\theta\sec(\theta)$
$d/d\theta\csc(\theta)$
$d/dx\sin^{-1}(x)$
$d/dx\cos^{-1}(x)$
$d/dx\tan^{-1}(x)$
$d/dx\cot^{-1}(x)$
$d/dx\sec^{-1}(x)$
$d/dx\csc^{-1}(x)$
Complex Number System
Analytic Function for $\sin(\theta)$
Analytic Function for $\cos(\theta)$
Analytic Function for $\csc(\theta)$
Analytic Function for $\sec(\theta)$
Analytic Function for $\tan(\theta)$
Analytic Function for $\cot(\theta)$
Analytic Function for $\sin^{-1}(x)$
Analytic Function for $\cos^{-1}(x)$
Analytic Function for $\csc^{-1}(x)$
Analytic Function for $\sec^{-1}(x)$
Analytic Function for $\tan^{-1}(x)$
Analytic Function for $\cot^{-1}(x)$
Unit Hyperbola Definitions
Hyperbolic Common Identities
Limits of Hyperbolic Functions
Derivatives of Hyperbolic Functions
Real Version of Euler's Formula
Analytic Hyperbolic Functions
Analytic Hyperbolic Inverses

|
|
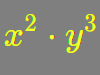
|

|
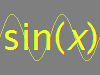
|

|

|

|

|