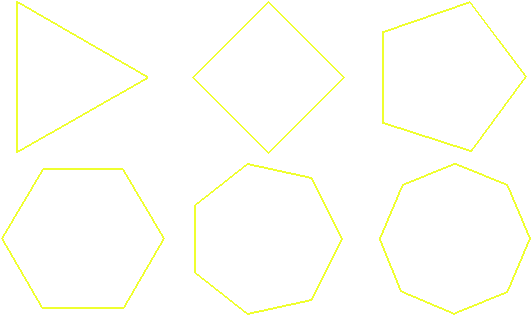
3.4.3 Regular Polygons
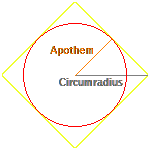
- $A=$ area
- $n=$ number of sides
- $s=$ length of sides
- $h=$ apothem
- $r=$ circumradius
| Perimeter |
$n·s$ |
| Area |
$n·s·h/2$ |
| Sum of angles |
$(n-2)·\pi$ |
| Angle $∡(h,r)$ |
$\pi/n$ |
| Circumradius |
$h·\sec \Big(\frac{\pi}{n}\Big) \land \frac{s}{2}·\csc \Big(\frac{\pi}{n}\Big)$ |
| Area using apothem |
$n·h^2·\tan \Big(\frac{\pi}{n}\Big)$ |
| Area using side |
$\frac{n·s^2}{4}·\cot \Big(\frac{\pi}{n}\Big)$ |
| Area using circumradius |
$n·r^2·\sin \Big(\frac{\pi}{n}\Big)·\cos \Big(\frac{\pi}{n}\Big)$ |
Proof of Circumradius
With respect to the center angle between the apothem and circumradius, use the corresponding
right angle definitions for $h$ = adjacent, $b/2$ = opposite, and $r$ = hypotenuse, and solve for $r$ in each case
$$\sec \Big(\frac{\pi}{n}\Big)=\frac{r}{h}\qquad\csc \Big(\frac{\pi}{n}\Big)=\frac{r}{s/2}$$
Proof of Area using Apothem
Set the two circumradius formulae equal to each other
$$h·\sec \Big(\frac{\pi}{n}\Big)=\frac{s}{2}·\csc \Big(\frac{\pi}{n}\Big)$$
Multiply by $h$, then divide by the cosecant function
$$h^2·\frac{\sec(\pi/n)}{\csc(\pi/n)}=\frac{s·h}{2}$$
Use the
right angle definitions of the secant and cosecant functions to simplify into the tangent function
$$\frac{\sec(\pi/n)}{\csc(\pi/n)}=\frac{r/h}{r/s}=\frac{s}{h}=\tan \Big(\frac{\pi}{n}\Big)$$
Substitute
$$h^2·\tan \Big(\frac{\pi}{n}\Big)=\frac{s·h}{2}$$
Multiply by the number of sides
$$n·h^2·\tan \Big(\frac{\pi}{n}\Big)=n·\frac{s·h}{2}$$
Proof of Area using Circumradius
Using the first circumradius equality, isolate $h$
$$h=\frac{r}{\sec(\pi/n)}$$
Substitute for $h$ in the equation for the area using the apothem
$$A=n·r^2·\frac{\tan(\pi/n)}{\sec^2(\pi/n)}$$
Use the
right angle definitions of the tangent and secant functions to simplify to sine and cosine
$$\frac{\tan(\pi/n)}{\sec^2(\pi/n)}=\frac{s/h}{r^2/h^2}$$
$$=\frac{s}{r}·\frac{h}{r}=\sin\Big(\frac{\pi}{n}\Big)·\cos\Big(\frac{\pi}{n}\Big)$$
Substitute
$$A=n·r^2·\sin\Big(\frac{\pi}{n}\Big)·\cos\Big(\frac{\pi}{n}\Big)$$
Proof of Area using Side Length
Substitute the second circumradius equality into the area using the circumradius equation, then expand
$$A=\frac{n·s^2}{4}·\csc^2\Big(\frac{\pi}{n}\Big)·\sin\Big(\frac{\pi}{n}\Big)·\cos\Big(\frac{\pi}{n}\Big)$$
Use the
right angle definitions to simplify the trig functions into cotangent,
$$\csc^2\Big(\frac{\pi}{n}\Big)·\sin\Big(\frac{\pi}{n}\Big)·\cos\Big(\frac{\pi}{n}\Big)$$
$$=\frac{r^2}{s^2}·\frac{s}{r}·\frac{h}{r}=\frac{h}{s}=\cot\Big(\frac{\pi}{n}\Big)$$
Substitute
$$A=\frac{n·s^2}{4}·\cot\Big(\frac{\pi}{n}\Big)$$