




| 1.2 « | 1.3 | » | ||||||

|
|
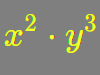
|

|
|

|

|

|

|
| $17+5=22$ | sum |
| $17-5=12$ | difference |
| $17·5=22$ | product |
| $\frac{17}{5}=3+\frac{2}{5}$ |
$17$: dividend $5$: divisor $17/5$: simplified fraction $3$: quotient $2$: remainder $3+2/5$: proper fraction |
| $\frac{x}{x_∘}+\frac{y}{y_∘}=1$ |
$x$: abscissa $x_∘$: horizontal axis intercept $+$: operator $y$: ordinate $y_∘$: vertical axis intercept $1$: value |
| $y=a·x^2+b·x+c$ |
$y$: dependent variable $a$: leading coefficient $x$: independent variable $2$: order $b$: coefficient $c$: constant |
| $(a+b·i)(a-b·i)=a^2+b^2$ |
( expression = expression ) ← equation factored form = expanded form $a$: real component $b·i$: imaginary component $(a±b·i)$: roots $(a+b·i)(conjugate)$ |
| $\sqrt[n]{x}$ |
$n$: $n$th root $x$: radicand |
|
$x/x_∘$ $y/y_∘$ $a·x^2$ $b·x$ $(a±b·i)$ $a^2$ $b^2$ $\sqrt[n]{x}$ |
terms |
| Even - symmetric about $y$-axis $$f(-x)=f(x)$$ |
 |
| Odd - symmetric about origin $$f(-x)=-f(x)$$ |
 |
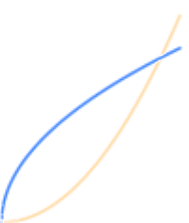
| Inverse - reflected about $y=x$ $$f^{-1}(f(x))=x$$ |
 |
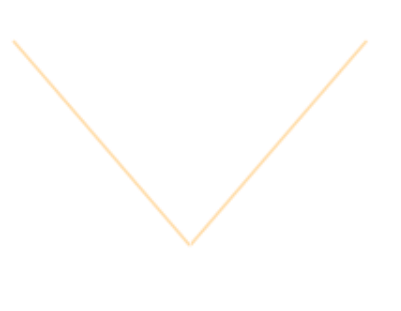
| Absolute value - magnitude; non-negative $$ |x| = \begin{cases} \phantom{-}x &x ≥ 0 \\ -x &x \lt 0 \end{cases} $$ |
 |
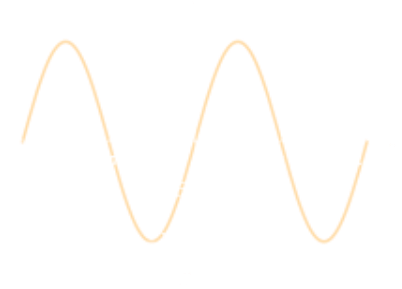
| Periodic - repeated segment ($P$) $$f(x+P)=f(x)$$ |
 |
| 1.2 « | 1.3 | » | ||||||

|
|
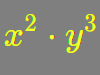
|

|
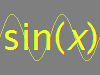
|

|

|

|

|